Efecto del extracto de Limnospira maxima sobre parámetros fisiológicos de Stevia Stevia rebaudiana Bert. y berenjena Solanum melongena L. bajo condiciones controladas
Effect of Limnospira maxima on physiological parameters of stevia Stevia rebaudiana Bert. and eggplant Solanum melongena L. under controlled conditions

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 4.0.
Mostrar biografía de los autores
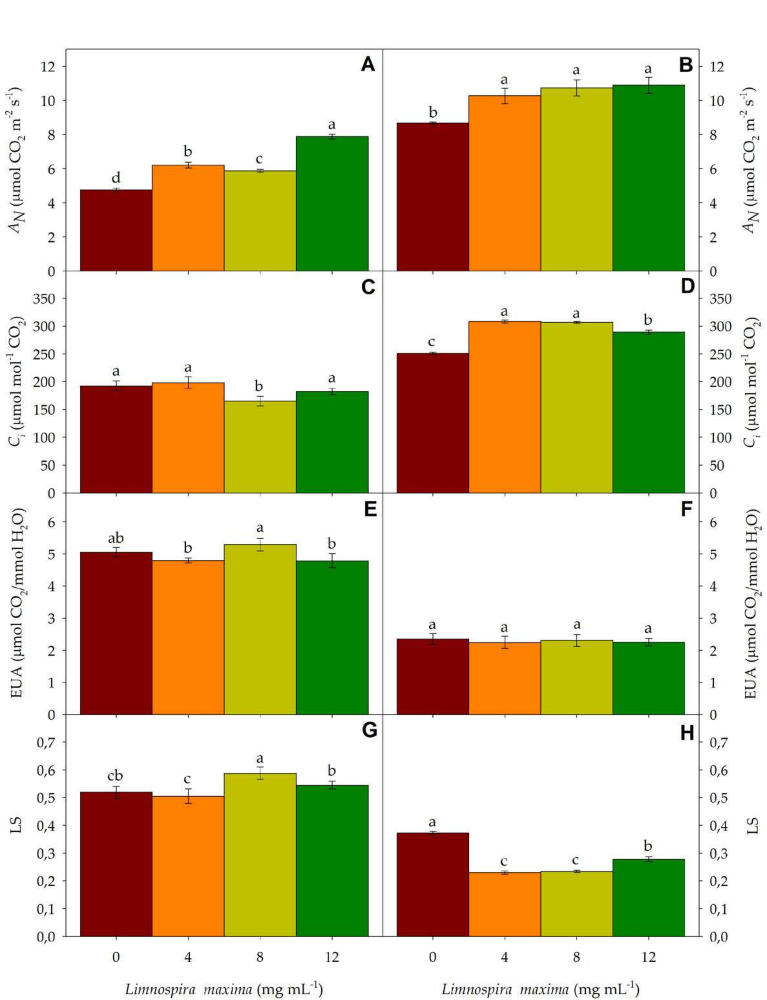
Una estrategia que podría disminuir parcial o totalmente el uso de fertilizantes de síntesis química es la aplicación de cianobacterias con potencial agrícola que promueven el crecimiento vegetal, lo que las potencia en la concepción de una agricultura sostenible. En el trabajo se evaluó el efecto de cuatro concentraciones de un extracto de Limnospira maxima (0, 4, 8, y 12 mg mL-1), sobre algunos aspectos fisiológicos de Stevia rebaudiana y Solanum melongena en casa vegetación. Los tratamientos se arreglaron bajo un diseño completo al azar y se midieron parámetros de intercambio gaseoso, fluorescencia de la clorofila a, caracteres biométricos y distribución de biomasa. Los resultados más importantes indicaron que en Stevia rebaudiana y Solanum melongena las tasas de fotosíntesis neta se incrementaron respectivamente en 40,03% y 22,45% cuando se aplicó la cianobacteria. Por otra parte, las plantas de ambas especies que fueron inoculadas requirieron de una menor cantidad de electrones para maximizar sus tasas de fotosíntesis, aumentaron el área foliar, la altura de planta y la distribución de biomasa en raíces y hojas. El indicador fisiológico más importante fue la fotosíntesis neta y este se correlacionó positivamente con casi todos los parámetros estudiados. Los resultados sugieren que el uso del extracto de L. maxima puede ser una alternativa biotecnológica de fertilización orgánica útil para el desarrollo de una agricultura sostenible.
Visitas del artículo 225 | Visitas PDF
Descargas
- Alharbi, K., Hafez, E., Omara, A. y Nehela, Y. 2023. Composted Bagasse and/or Cyanobacteria-Based Bio-Stimulants Maintain Barley Growth and Productivity under Salinity Stress. Plants 12(9): 1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12091827
- Britos, A., Alonso, N. y Álvarez, R. 2022. Fertilización química con corrección de pH en suelos ácidos y rendimiento por hectárea de Brachiaria brizantha. Revista Veterinaria 33(2): 130. https://doi.org/10.30972/vet.3326340
- Cantero, R., Espitia N., Cardona, C., Vergara, C. y Araméndiz, H. 2015. Efectos del compost y lombriabono sobre el crecimiento y rendimiento de berenjena Solanum melongena L. Revista de Ciencias Agrícolas 32(2): 56-67. https://doi.org/10.22267/rcia.153202.13
- Chen, Y., Chen, H., Chen, R., Yang, H., Zheng, T., Huang, X. y Fan, G. 2023. The Impacts of Nitrogen Accumulation, Translocation, and Photosynthesis on Simultaneous Improvements in the Grain Yield and Gluten Quality of Dryland Wheat. Agronomy 13(5): 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13051283
- Deviram, G., Mathimani, T., Anto, S., Ahamed, T., Ananth, D. y Pugazhendhi, A. 2020. Applications of microalgal and cyanobacterial biomass on a way to safe, cleaner and a sustainable environment. Journal of Cleaner Production 253: 119770. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119770
- Ekeuku, S., Chong, P., Chan, H., Mohamed, N., Froemming, G. y Okechukwu, P. 2022. Spirulina supplementation improves bone structural strength and stiffness in streptozocin-induced diabetic rats. Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine 12(3): 225-234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcme.2021.07.010
- Ertani, A., Nardi, S., Francioso, O., Sanchez-Cortes, S., Foggia, M. y Schiavon, M. 2019. Effects of Two Protein Hydrolysates Obtained From Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) and Spirulina platensis on Zea mays (L.) Plants. Frontiers in Plant Science 10: 954. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00954
- Geries, L. y Elsadany, A. 2021. Maximizing growth and productivity of onion (Allium cepa L.) by Spirulina platensis extract and nitrogen-fixing endophyte Pseudomonas stutzeri. Archives of Microbiology 203(1): 169-181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-020-01991-z
- Hernández-Fernández, I. A., Jarma-Orozco, A. y Pompelli, M. F. 2021. Modelos alométricos não destrutivos para estimação da área foliar de stevia: uma análise completa e profunda. Horticultura Brasileira 39: 205-215. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/s0102-0536-20210212
- Mala, R., Ruby, A., Mahalakshmi, R. y Rajeswari, S. 2017. Agronomic Biofortification of Amaranthus dubius with Macro Nutrients and Vitamin A. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering 225: 012214. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/225/1/012214
- Martínez-Vega, J., Villafaña-Estarrón, E. y Escalante, F. 2022. Comparative Study of the Efficiency of Additives in the Extraction of Phycocyanin-C from Arthrospira maxima Using Ultrasonication. Molecules 28(1): 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010334
- Mógor, Á., De Oliveira, J., Mógor, G. y Bocchetti, G. 2018. Bioactivity of Cyanobacterial Biomass Related to Amino Acids Induces Growth and Metabolic Changes on Seedlings and Yield Gains of Organic Red Beet. American Journal of Plant Sciences 09(05): 966-978. https://doi.org/10.4236/ajps.2018.95074
- Muratova, A., Gorelova, S., Golubev, S. y Gins, M. 2023. Rhizosphere Microbiomes of Amaranthus spp. Grown in Soils with Anthropogenic Polyelemental Anomalies. Agronomy 13(3): 759. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13030759
- Mutale-joan, C., Redouane, B., Najib, E., Yassine, K., Lyamlouli, K., Laila, S., Zeroual, Y., y Hicham, E. 2020. Screening of microalgae liquid extracts for their bio stimulant properties on plant growth, nutrient uptake and metabolite profile of Solanum lycopersicum L. Scientific Reports 10(1): 2820. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-59840-4
- Nowicka-Krawczyk, P., Mühlsteinová, R. y Hauer, T. 2019. Detailed characterization of the Arthrospira type species separating commercially grown taxa into the new genus Limnospira (Cyanobacteria). Scientific Reports 9(1): 694. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-36831-0
- Lima de Oliveira, R. L., Robson Moreira, A., Vanderlane Albuquerque da Costa, A., Castro de Souza, L., Souza Lima, L. G. y Lima da Silva, R. T. 2015. Modelos de determinação não destrutiva de área foliar de feijão caupi Vigna unguiculata (L.). Global Science and Technology 8(2): 17-27
- Olorunwa, O., Adhikari, B., Shi, A. y Barickman, T. C. 2022. Screening of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.) genotypes for waterlogging tolerance using morpho-physiological traits at early growth stage. Plant Science 315: 111136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2021.111136
- Orona-Navar, A., Aguilar-Hernández, I., Nigam, K. D. P., Cerdán-Pasarán, A. y Ornelas-Soto, N. 2021. Alternative sources of natural pigments for dye-sensitized solar cells: Algae, cyanobacteria, bacteria, archaea and fungi. Journal of Biotechnology 332, 29-53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2021.03.013
- Pineda-Rodriguez, Y., Pompelli, M., Jarma-Orozco, A., Rodríguez, N. y Rodriguez-Paez, L. 2023. A New and Profitable Protocol to DNA Extraction in Limnospira maxima. Methods and protocols 6(4): 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps6040062
- Ren, H., Xu, S., Zhang, F., Sun, M. y Zhang, R. 2023. Cultivation and Nitrogen Management Practices Effect on Soil Carbon Fractions, Greenhouse Gas Emissions, and Maize Production under Dry-Land Farming System. Land 12(7): 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12071306
- Rodriguez-Paez, L., Jimenez-Ramirez, A., Pompelli, M., Pineda-Rodriguez, Y., Jarma-Orozco, A., Jaraba-Navas, J., Aramendiz-Tatis, H., Combatt-Caballero, E., Oloriz-Ortega, M. y Rodríguez, N. 2023. Physiological and Enzymatic Evaluation of Selected Genotypes of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni. Agronomy 13(2): 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13020403
- Shedeed, Z., Gheda, S., Elsanadily, S., Alharbi, K. y Osman, M. 2022. Spirulina platensis Biofertilization for Enhancing Growth, Photosynthetic Capacity and Yield of Lupinus luteus. Agriculture 12(6): 781. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12060781
- Soppelsa, S., Kelderer, M., Casera, C., Bassi, M., Robatscher, P., Matteazzi, A. y Andreotti, C. 2019. Foliar Applications of Biostimulants Promote Growth, Yield and Fruit Quality of Strawberry Plants Grown under Nutrient Limitation. Agronomy 9(9): 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9090483
- Supraja, K., Behera, B. y Balasubramanian, P. 2020. Efficacy of microalgal extracts as biostimulants through seed treatment and foliar spray for tomato cultivation. Industrial Crops and Products, 151: 112453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.112453
- Toribio, A., Suárez-Estrella, F., Jurado, M., López, M., López-González, J. y Moreno, J. 2020. Prospection of cyanobacteria producing bioactive substances and their application as potential phytostimulating agents. Biotechnology Reports 26: e00449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2020.e00449
- Xu, C. y Leskovar, D. 2015. Effects of A. nodosum seaweed extracts on spinach growth, physiology and nutrition value under drought stress. Scientia Horticulturae 183: 39-47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2014.12.004
- Yang, Z., Tan, S., Yang, Q., Chen, S., Qi, C., Liu, X., Liang, J. y Wang, H. 2023. Nitrogen Application Alleviates Impairments for Jatropha curcas L. Seedling Growth under Salinity Stress by Regulating Photosynthesis and Antioxidant Enzyme Activity. Agronomy 13(7): 1749. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13071749
- Yassen, A., Essa, E. y Zaghloul, S. 2019. The role of vermicompost and foliar spray of Spirulina platensis extract on vegetative growth, yield and nutrition status of lettuce plant under sandy soil. Research Journal of Agriculture and Biological Sciences 14: 1-7. https://doi.org/10.22587/rjabs.2019.14.1.1
- Yu, M., Sun, P., Huang, X., Zha, Z., Wang, X., Mantri, N., Lou, H., Jiang, B., Shen, Z., Sun, Y. y Lu, H. 2023. Interacting Effects of CO2, Temperature, and Nitrogen Supply on Photosynthetic, Root Growth, and Nitrogen Allocation of Strawberry at the Fruiting Stage. Agronomy 13(5): 1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13051353
- Zewail, R., Ali, M., El-Gamal, I., Al-Maracy, S., Islam, K., Elsadek, M., Azab, E., Gobouri, A., ElNahhas, N., Mohamed, M. y El-Desouky, H. 2021. Interactive Effects of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Inoculation with Nano Boron, Zinc, and Molybdenum Fertilization on Stevioside Contents of Stevia (Stevia rebaudiana, L.) Plants. Horticulturae 7(8): 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7080260
- Zheng, X., Zhang, B., Pan, N., Cheng, X. y Lu, W. 2023. Hydrogen Sulfide Alleviates Cadmium Stress by Enhancing Photosynthetic Efficiency and Regulating Sugar Metabolism in Wheat Seedlings. Plants 12(13): 2413. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12132413
- Zou, T. y Zhang, J. 2020. A New Fluorescence Quantum Yield Efficiency Retrieval Method to Simulate Chlorophyll Fluorescence under Natural Conditions. Remote Sensing 12(24): 4053. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12244053